Some users may face the problem of LSAISO.exe The process (isolated LSA) experiences high CPU usage on a Windows 10 computer. The process is associated with Security Guard and Key Guard. In this article, we are looking at the possible cause and recommended solution to this problem.
LSAISO process high CPU usage
VSM uses isolation modes called Virtual confidence levels (VTL) to protect IUM processes (also called trustlets). IUM processes such as LSAISO run in VTL1 while other processes are running VTL0. The memory pages of the processes that run in VTL1 are protected from malicious code that runs in VTL0.
The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process is responsible for managing local system policy, user authentication and auditing, while managing sensitive security data such as hashes of password and Kerberos keys.
To use the security benefits of VSM, the LSAISO trustlet that runs in VTL1 communicates via an RPC channel with the LSAISO process which runs in VTL0. LSAISO secrets are encrypted before being sent to LSASS, and LSAISO pages are protected from malicious code running in VTL0.
Possible cause of high CPU usage by the LSAISO process
In Windows 10, the LSAISO process works like Isolated user mode (IUM) in a new security environment called Virtual secure mode (VSM).
Applications and drivers that attempt to load a DLL (Dynamic Link Library) into an IUM process, inject a thread, or provide user-mode APC can destabilize the entire system. This destabilization can trigger high usage of the LSAISO processor in Windows 10.
How to solve the problem of high CPU usage by the LSAISO process
To resolve this problem, Microsoft recommend using one of the following methods.
- Use the elimination process.
- Check the queued APCs.
Now let's see the details of the two recommended solutions.
1) Use the disposal process
It is common for some applications (such as antivirus programs) to inject queued DLLs or APCs into the LSAISO process. This causes the LSAISO process to use high CPU usage.
In this scenario, the "elimination process"The troubleshooting method requires that you disable apps and drivers until the CPU peak is attenuated. After determining which software is causing the problem, contact the vendor for an update. software day.
2) Check the queued APCs
In this scenario, you must first download the free Windows debugging tool (WinDbg). the the tool is also included in the Windows driver kit (WDK).
Once you've downloaded the WinDbg tool, you can then follow the steps outlined below to determine which driver queues an APC to LSAISO.
The procedure is as follows:
Note: A full memory dump is not recommended as it would require decryption if VSM is enabled on the system.
To enable kernel dump, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R. In the Run dialog box, type Control system, press Enter to open the System applet in Control Panel, then select Advanced system settings.
- On the Advanced tab of System properties dialog box select settings in the Startup and recovery zoned.
- in the Startup and recovery dialog box select Emptying the kernel memory in the Write debugging information the drop-down list.
- Take note of Dump file location to use in step 5, then click D & #39; agreement.
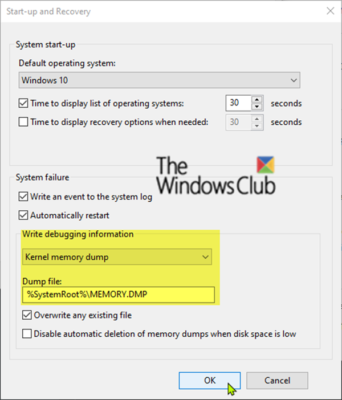
2. Click on the beginning button, locate and click Windows kits from the Start menu, then select WinDbg (x64 / x86) to launch the tool.
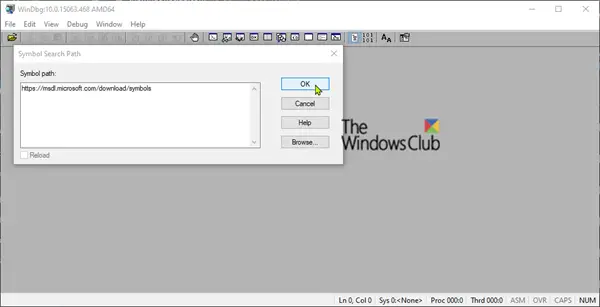
3. On the File menu click Symbol file path, add the address path below for Microsoft Symbol Server to Symbol path and click D & #39; AGREEMENT.
https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
4. Then on the File menu click Open Crash Dump.
5. Navigate to the location of the kernel dump file that you noted in step 1, then select Open. Check the date on the .dmp to make sure it was created during this troubleshooting session.
6. In the Order window type ! apc, press Enter.
You will receive a similar output, as shown below.
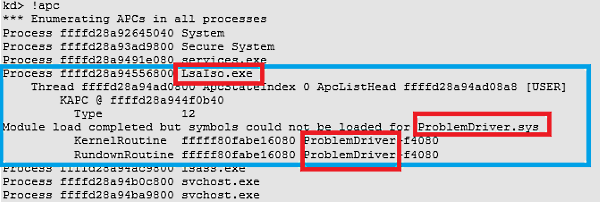
7. Search the results for LsaIso.exe. If a pilot named "
If no driver is listed under Lsaiso.exe, it means that the LSAISO process has no APC queued.
That's it!
