Network packets or packets are small units of data that pass through a network. When you send information, the data is divided into small packets and then recombined at the other end. The loss of these packets is called packet loss, that is, they have not reached their destination. These packets can pass through any type of network – WiFi or Ethernet. The loss through the WiFi network is much greater, and in this article we will talk about what is WiFi packet loss and how do you test and correct it?
What is WiFi packet loss?
There are many reasons why the loss of WiFi packets can occur. It can be radio frequency interference, weak signal, distance between source and signal, and even faulty cables and hardware. Since the signal is in the air, the risk of data loss is even higher. Fortunately, technology has advanced with better source and reception, but data loss still occurs.
Too much packet loss can slow down the Internet experience. So, if your Internet is working properly, here are some ways to test and fix the loss of WiFi packets.
How to test and fix WiFi packet loss
Before starting the tests, if all goes well, you will have two options. Faulty cables and hardware. This is something that can be diagnosed by changing the wires and the router or repeater.
Packet loss testing and diagnosis
When data is sent, it jumps from one network to another. Data loss occurs between hops or congestion at the junction. To find out where packet loss occurs, you need to know which parts of the connection are slow and the networks are causing the problem.
1]Traceroute and Ping
Traceroute is a command where a sample of data is sent to the destination, and the result for each hop with the IP address is displayed. If there is a data loss, it will be marked with a star, then followed by an expired request. In the traceroute results, the first initial hops are made from your computer to the router, then to your ISP server. If you see time in these paths, you know the problem is on your side.
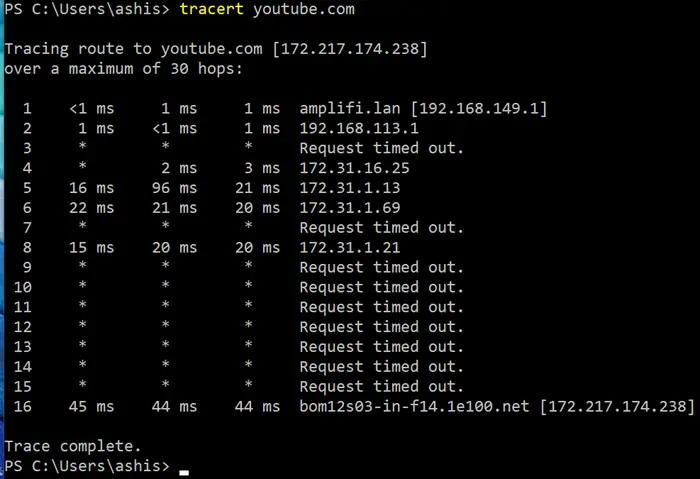
Ping, on the other hand, involves finding out if the host is available and measuring the time required for the response. The advantage of using ping is that you have an idea of the percentage of data loss.
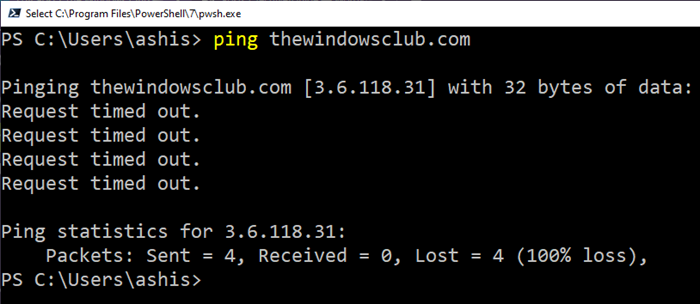
2]Microsoft network monitor
It is a free tool available in Windows (netmon.exe) where you select the network card and start capturing the data that comes out and on the computer. It is useful for capturing, viewing and analyzing protocol mail traffic and other system messages. It can both troubleshoot and test protocol implementations. Useful for pros.
Besides these, you can consult the list of free network monitoring tools, network managers and eToolz
Fixed loss of WiFi packets
Distance between source and signal
One of the main reasons for losing network packets is that the distance between the source and the signal is too great. If your device, laptop or phone, is far away or is in a blind hotspot, this will cause many packet losses. There are two solutions. You can choose to close the source, or you can add repeaters or get a powerful router to make sure the blind spots are covered.
Mesh routers are a good example that can help you cover more area. Some routers offer applications and services that can help you determine the coverage area and blind spots.
Radio frequency interference
These are the main cause of data loss. Routers are allowed to operate in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz range. While the former offers a wide range, the latter offers better resistance. That said, wireless devices meet 802.11 (a / b / g / n / ac) standards.
Take a building example, if there are too many radio devices in this range, then packet loss is inevitable. When an 802.11 box hears another signal in the range and in almost the same direction, it delays transmission until the signal weakens or stops. If interrupted too often, this will result in a retransmission request, which will reduce performance and throughput.
This problem has been resolved with the 802.11n standard. It uses multiple radios from a single access point to transmit multiple WiFi streams in different directions simultaneously. This increases the chances of lossless data transmission.
The ideal solution is therefore to switch to a more intelligent router, which offers a signal / noise ratio (SNR). The increasing gain in one direction may not cut, and therefore you need a router with adaptive antenna arrays and software algorithms to obtain the gain.
Related: How to increase WiFi speed, signal strength and coverage area
Upgrade or replace Ethernet cables

If you have been using a network cable to the router for a very long time, you may want to upgrade it. For example, the category Cat 5 offers a speed of 100 MBPS while the category 6a offers 10,000 MPBS every 100 meters.
Losing WiFi packets on the network is nothing new, but with so many WiFi devices around, high multimedia consumption, it has become more common. The need for a smarter router in software and hardware is the demand of the day. I hope the message was easy to follow and that you were able to resolve or understand what was causing the loss of WiFi packets.
Related reading: Change the sensitivity of WiFi roaming to improve WiFi reception and performance.