Random access memory (RAM) works with the processor to quickly access temporary files to efficiently run programs on your computer. You may experience program sluggishness and crashes when the memory does not work normally.
Removing RAM modules from desktop computers is easy, but impossible from modern laptops. But before physically inspecting them, Windows includes the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to troubleshoot memory-related issues on your PC. Here’s a guide to everything you need to know about using the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool on Windows 11.
Like other tools in Windows, there are many ways to access the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool. However, to keep things simple and easy to understand, we’ll cover how you can easily access the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool using the Run utility, and then how you can use it on your PC.
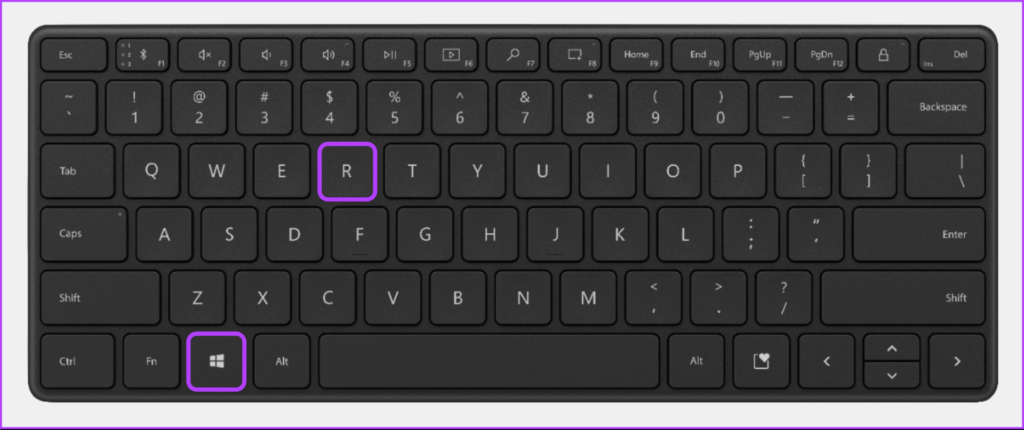
Step 1: Press Windows + R keys simultaneously to access the Run utility.

2nd step: When a Run dialog box appears on your screen type mdsched.exe. Then click OK.


Step 3: You should see a Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool window appear on your screen with two options:
- Click on the “Restart now and check for problems (recommended)” option if you want to restart your PC and fix memory related issues immediately.
- Click the “Check for problems the next time I start my computer” option if you want to schedule the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to run the next time you start your PC.


We selected the first option; you can choose the second option if necessary. Whichever option you choose, once your PC restarts, the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool will automatically begin scanning your system for memory-related issues in Standard mode.


Running a two-pass scan in Standard mode should be enough to uncover any memory errors in most cases. However, if you want to change the scan options to Basic or Extended and change the number of scan passes, press the F1 key on your keyboard to access more options.


Note that you will need to press the Tab key on your keyboard to cycle through the various scan options, F10 to apply the new changes, or Esc to go back and discard the changes.
How to Check Memory Diagnostic Results
When the scan is complete, your PC will restart and a pop-up notification with the results should appear in the lower right corner of the desktop view. However, it is a bit random and does not give you a detailed overview of the scan results. In such cases, you will need to check Event Viewer.
Here’s how to check Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool results using Event Viewer:
Step 1: Press Windows key + S to launch Windows Search and type Event Viewer. Then from the result that appears, click Open.


2nd step: When an Event Viewer window opens, click Windows Logs followed by System. Then click Search in the rightmost pane.


Step 3: When a Find dialog box appears on the screen, type MemoryDiagnostics-Results. Then click Find Next.
Clicking Find Next will help you find the most recent memory diagnostic report. If you want to search for older reports, keep clicking the Find Next button.


Step 4: When you find the relevant report using the Find Next button, click Cancel.


Step 5: You will see the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool scan result on your screen. Additionally, you can click the Details tab to find even more detailed results for analysis.


If there are no problems with the memory installed on your system, you will receive a message that Windows Memory Diagnostic has tested the computer’s memory and found no errors. But if errors are detected, you will find details about the problem with the RAM installed in your system.
You can clean and reinstall the RAM sticks. Then, run a Windows diagnostic scan again to check if the issues are resolved. If that doesn’t help, it might be time to replace your system’s old RAM.
To replace or upgrade your PC’s RAM, see our guide on how to find available RAM slots on Windows 11 as well as the four best ways to check RAM size on Windows 11.
That’s all. After following all the steps above, you should be able to quickly fix memory leaks or other RAM-related issues on your Windows 11 PC using the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool .
